Probability
Probability is interchangeable with proportion; although one is theoretical, the other arithmetical.
Axiomatic Probability
- Probability space
- Conditional probability
- Total probability equation, Bayes formular
- Independence
Random Variable
- Measurable function on probability space
- Distribution: CDF, PDF, PMF
- Integration (Expectation) - Riemann-Stieltjes integral
- Characteristic function and moments
Function Analytic Approach to Probability
- Conditional expectation
- Hierarchical models
- Independence as an assumption and simplification.
- Covariance and correlation
Special topics
- Inequalities and Identities
- Gaussian Random Variables
- Transformation and Decomposition
- Statistics of Extremes
Random Process
Note: Mathematical theories go complicated very fast; in fact, the description of random processes is already impractical and requires too much information. To put the mathematical model into practical use, vast simplification is needed.
Stochastic Analysis
- Stochastic Convergence
- Limit Theorems
-
Random Process Analysis
- Convergence
- Continuity
- Differentiability
- Integrability
-
Spectral Representation
- K-L expansion
- PCE
Random Processes
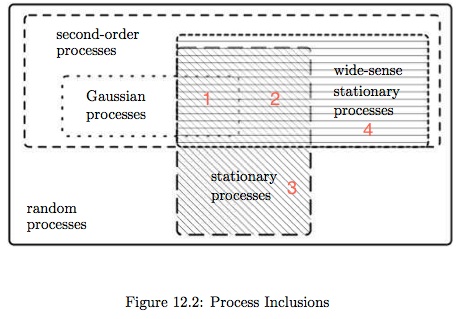 (Ref: Scholtz, P266.)
(Ref: Scholtz, P266.)
Nassim Nicholas Taleb, Skin in the game. "Ergodicity is not statistically identifiable, not observable, and there is no test for time series that gives ergodicity, similar to Dickey-Fuller for stationarity (or Phillips-Perron for integration order)." "If your result is obtained from the observation of a time series, how can you make claims about the ensemble probability measure?"
Appendices
- Reference Distribution
- Distributions from Discrete Random Process
- Distributions from Continuous Random Process
- Asymptotic Distributions
- Gaussian-related Distributions
Fourier Transforms, Z-transform
Table: Fourier Transform and Its Inverse Transform as the Integral Transforms Defined by Kernels. (In the form of $a e^{bixy}$, where $a$ is normalization and $b$ is oscillatory factor.)
| Convention | Forward kernel | Inverse kernel |
|---|---|---|
| physics | $e^{-ixy}$ | $(2\pi)^{-1}e^{ixy}$ |
| physics, symmetric | $(2\pi)^{-1/2} e^{-ixy}$ | $(2\pi)^{-1/2} e^{ixy}$ |
| mathematics | $e^{-2\pi ixy}$ | $e^{2\pi ixy}$ |
| general | $│b│^{1/2}(2\pi)^{(-1+a)/2}e^{-ibxy}$ | $│b│^{1/2}(2\pi)^{(-1-a)/2}e^{ibxy}$ |
Sinc function $\text{sinc}(x) = \frac{\sin x}{x}$, $x \ne 0$. Normalized sinc function $\text{sinc}(x) = \frac{\sin(\pi x)}{\pi x}$, $x \ne 0$, because its integral on the real line equals one: $\int_{-\infty}^\infty \frac{\sin(\pi x)}{\pi x} = 1$. Rectangular function is the centered unit-length indicator function: $\text{rect}(x) = 1(|x| \le 1/2)$. The Fourier transform (in math convention) of the normalized sinc / rectagular function is the rectagular / normalized sinc function. The Fourier transform (in physics convention) of the sinc function is the constant function that equals pi in between -1 and 1: $\int_{-\infty}^\infty e^{-ixt} \frac{\sin x}{x} = \pi \cdot 1(|t| \le 1)$.
Table 1: Interpretations of probability
| Ontic (实存) probability | Epistemic (认识) probability |
|---|---|
| long run frequency | objective degree of belief |
| single-case propensity | subjective degree of belief |